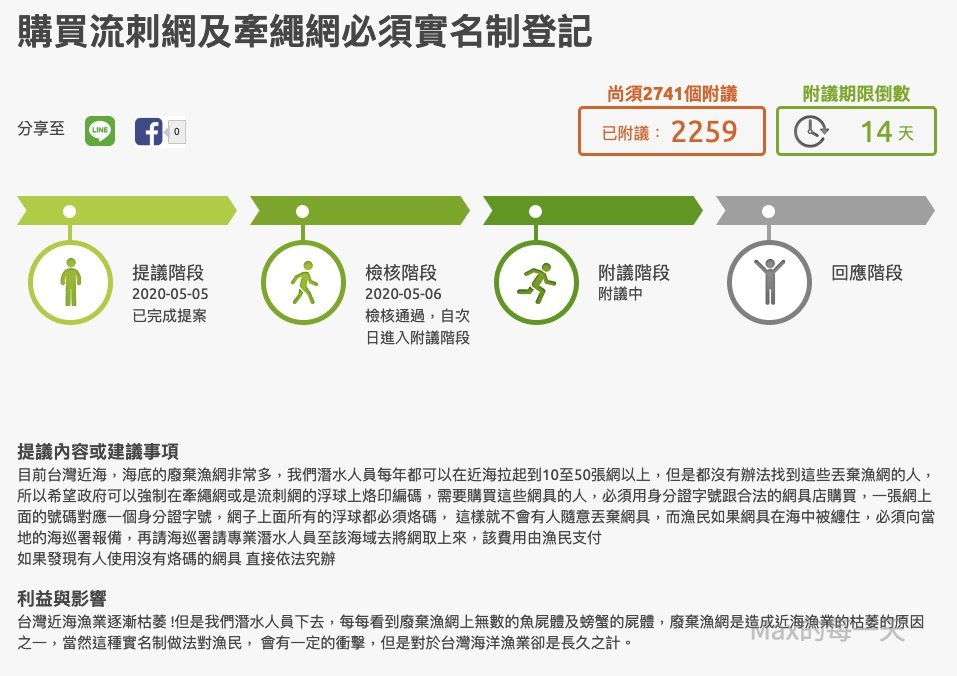
請大家幫忙「附議」,謝謝。附議網址:https://join.gov.tw/idea/detail/cc29d44d-bb1b-406f-aca9-6ea35e07d8b8
相關報導:
- 推動實名制 「愛與皮鞭」齊下 兩年讓八成刺網漁船退場(2019-09-11)
https://www.businesstoday.com.tw/article/category/80393/post/201909110020/ - 【死亡之網】賺錢不顧下一代 流刺網船:頂多我兒子不吃魚(2019/08/19)
https://www.chinatimes.com/realtimenews/20190819000748-260402
流刺網:
流刺網是一種捕魚方法,主要用於捕撈洄游性魚類。流刺網使用一層或多層塑膠絲所織成的長方形網片,一般會將多張網片結合在一起,上緣繫多個海綿塑膠所製的浮子,下端配附鉛製沉子,垂直張開設於接近海平面附近的位置,等待魚類游入而被網目纏住。因為會隨海流移動,而且被纏住的魚像刺一樣掛在網上,故稱「流刺網」。
流刺網的殺傷力很大,大型流刺網往往由大、中、小網目的三層網子所構成,不論是大魚、小魚都全部落網,會造成生態浩劫。因此各國陸續禁用流刺網捕魚。
流網:
流刺網是刺網的一種,結構簡單像圍牆漂浮在海中,由數十至數百枚長方形網片串連而成,每單片網長約30公尺,網高約15公尺,全組最長網長可達50餘公里。作業時,將數百或數千公尺長的刺網撒入海裡,漁網上緣繫著小浮標 (曝光),下擺連著鉛錘線 (雷腳),刺網入水後,一端藉浮標浮力懸浮在水面上;另端藉鉛錘線重力垂下海水裡,使漁網在水中張開,整座網具無沉底支點,而隨著潮流漂動。漁獲的方式可分為刺入及纏繞,主要漁獲以刺入的為主,用來在大洋中撈捕魷魚或高度洄游的鮪魚,比傳統使用之釣具,效率高出數倍而節省能源。但流刺網綿延的細網漂浮於海面上,捕獲洄游魚類的同時,也危害到過往船隻的航行安全,且流刺網無選擇地捕獲海中的生物像鯨魚、鯊魚、海獅、海狗、海豚都可能纏在魚網上。有些海鳥則是想吃流刺網上的魚或潛入海中抓魚不慎一起被流刺網捕獲。經過多年的國際間爭議與協商,流刺網的爭議終於因聯合國通過自一九九三年一月一日起,全面暫停公海使用流刺網之決議,而暫告一段落。
目前台灣亦明文規定禁止我國籍漁船於公海上利用流刺網捕魚,但近海漁業仍有相當多利用流刺網作業的漁船。
刺網漁業管制:
刺網分單層與多層,多層刺網可能由二、三、四重以上不同網目之刺網組成,具有漁獲效率高之優點,但也因容易混獲幼小魚種、網具容易纏絡礁岩地區破壞棲地,甚至網具流失變成死亡之牆,政府對其應有相當之管制。目前管理規定如下:
* 在我國200浬內海域從事流網作業須經主管機關核准,且作業漁船總噸數不得超過100噸,使用之流網網具長度不得超過2.5公里。
* 我國漁船未經核准經營流網漁業,不得改造為流網漁船或加裝流網設備或攜帶流網網具或設備。
* 各縣市政府對刺網使用,亦分別訂定禁漁區或禁漁期或限制多層刺網使用等規範。
Drift net 英文的Wiki:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drift_netting
Drift netting is a fishing technique where nets, called drift nets, hang vertically in the water column without being anchored to the bottom. The nets are kept vertical in the water by floats attached to a rope along the top of the net and weights attached to another rope along the bottom of the net.[1] Drift nets generally rely on the entanglement properties of loosely affixed netting. Folds of loose netting, much like a window drapery, snag on a fish’s tail and fins and wrap the fish up in loose netting as it struggles to escape. However the nets can also function as gill nets if fish are captured when their gills get stuck in the net. The size of the mesh varies depending on the fish being targeted. These nets usually target schools of pelagic fish.
Traditionally drift nets were made of organic materials, such as hemp, which were biodegradable. Prior to 1950, nets tended to have a larger mesh size.[2] The larger mesh only caught the larger fish, allowing the smaller, younger ones to slip through. When drift net fishing grew in scale during the 1950s, the industry changed to synthetic materials with smaller mesh size.[1] Synthetic nets last longer, are odourless and may be nearly invisible in the water, and do not biodegrade.[2] Most countries regulate drift net fisheries within their territories. Such fisheries are also often regulated by international agreements.
Drift net fishing became a commercial fishing practice because it is cost effective. Nets can be placed by low-powered vessels making it fuel efficient. Drift nets are also effective at bringing in large amounts of fish in one catch.[1]
Prior to the 1960s net size was not limited, and commercially produced nets were commonly as long as 50 kilometres (31 mi).[3] In 1987 the U.S. enacted the Driftnet Impact, Monitoring, Assessment and Control Act limiting the length of nets used in American waters to 1.5 nautical miles (≈1.7 miles, ≈2.778 km). In 1989 the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) placed a moratorium on the practice of drift net fishing.[4] In 1992 the UN banned the use of drift nets longer than 2.5 km long in international waters.[5]


